This is a Professional feature: download PyCharm Professional to try.
PyCharm allows running the current run/debug configuration while attaching a Python profiler to it. Note that the UML plugin that is bundled with PyCharm should be enabled.
There's a community edition (with limited features) that's free to use. You can also get a 30-day trial of the Professional edition. In PyCharm Professional and GoLand, debugging is supported starting from version 2021.1. Does JetBrains have plans for a stand-alone Rust IDE? There are no such plans at the moment because we don't see additional value a separate Rust IDE would bring. I'm using PyCharm Professional edition and tried to use the profiler, but the result is only a large list of irrelevant functions that I've never heard of. I cannot find profile button in Pycharm Community 2020.2 in CentOS. How to execute a program or call a system command from Python.
If you have a yappi profiler installed on your interpreter, PyCharm starts the profiling session with it by default, otherwise it uses the standard cProfile profiler.
Besides these two tracing profilers, PyCharm supports also sampling (statistical) profiler vmprof, which should be installed on the selected Python interpreter. If you are Windows 64 bit user, you have to install Python 32 bit, to make vmprof work. Install 32-bit Python as described on the page Python Releases for Windows.
A profiler runs in the following order: vmprof, yappi, cProfile.
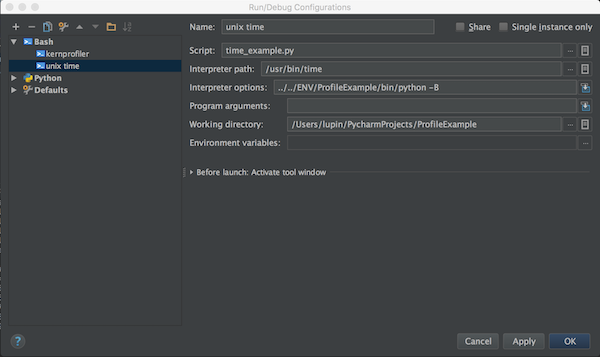
Start the profiling session
Click on the main toolbar and select Profile or select the same command from Run in the main menu.
Ensure that the profiler has started in the dedicated tab of the Run tool window.
Item Description Saves the profiling results in the .pstat file for cProfile profiler and the .prof file for vmprof. Stops the profiler. Closes the profiler tab.
Work with the profiling results
On the toolbar of the profiler tab in the Run tool window, click .
Inspect the profiling results:
The snapshot is saved to the default location under JetBrains/snapshots on Windows and ~/Library/Caches/JetBrains//snapshots on macOS. For CProfiler, it is saved as .pstat file. The file opens in the .pstat tab in the editor, which consists of two tabs: Statistics and Call Graph:
Item Description Name The name of the function.
Call Count Number of calls of the chosen function. Time Execution time of the chosen function plus all time taken by functions called by this function. The percentage of time spent in this call related to time spent in all calls in the parentheses. Own Time Own execution time of the chosen function. The percentage of own time spent in this call related to overall time spent in this call in the parentheses. Tip: To search for a particular file in the Name column of the Statistics table, click any cell and start typing the target name. The Search field appears in the header of the column so that you can edit the search criteria.
The snapshot is saved to the default location under JetBrains/snapshots on Windows and ~/Library/Caches/JetBrains//snapshots on macOS. For vmprof, it is saved as .prof file.
The file open in the .pstat tab in the editor, which consists of three tabs: Statistics, Call Graph, and Call Tree
Tip:Jump to the source code of any file and preview the Profile lines profiling results in the gutter. Lines consuming more processor time are marked yellow and red.
Jump to the source code
To navigate to the source code of a certain function, right-click the corresponding entry on the Statistics tab, and choose Navigate to Source from the context menu:
The source code of the function opens in the editor.
View the Call Graph
To navigate to the call graph of a certain function, right-click the corresponding entry on the Statistics tab, and choose Show on Call Graph from the context menu.
The Call Graph tab opens with the selected function:
Note the color codes on the Call Graph. The functions marked red consume more time; the fastest functions are green.
Use the toolbar buttons to work with the graph:
Item Description Click this icon to increase the scale of the diagram. Alternatively, press NumPad+. Click this icon to decrease the scale of the diagram. Alternatively, press NumPad-. Click this icon to restore the actual size of the diagram. Click this icon to make the contents fit into the current diagram size. Click this icon to apply the current layout, selected from the diagram context menu. Click this icon to save the current diagram in the specified location as xml file. Click this icon to save the diagram in an image file with the specified name and path. The possible formats are: jpeg, png, svg, svgz, or gif. Click this icon to print the diagram.
Review the existing cProfile snapshots

From the main menu, choose Tools | Open CProfile snapshot.
In the Select PStat file dialog, choose the desired file with the extension pstat.
The profiling results open in the .pstat tab in the editor.
PyCharm and Jupyter are two very popular environments among Python developers and data scientists. Both these environments offer their own set of advantages. But which between the two should a data scientist pick?
Both PyCharm and Jupyter have their advantages in data science. Jupyter is more suitable as a prototyping tool for prototyping models and doing a quick analysis of data. PyCharm is generally suitable for building complex multi-layered applications that can analyze large data sets.
In this article, we will explore this subject in detail. We will start off by looking at the key features of each of these platforms. Next, we will differentiate between them and then finally discuss which of them is the better choice for data science.
PyCharm: Key Features
PyCharm is a Python IDE developed by JetBrains. It is one of the most popular Python IDEs among developers, and there are several reasons behind this.
First and foremost, PyCharm has one of the best code editors among all the Python IDEs. It features all the basic features like code analysis, quick fixes, syntax/error highlighting as well as additional features like code folder, auto-code generation, auto-indentation, etc. Navigating across your codebase is also incredibly easy with PyCharm thanks to features like an easy location for the usage of a symbol.
Additional features include a powerful debugger that comes with a graphical interface as well as integrated unit testing capability that presents the results graphically. A cool version control system is integrated within PyCharm, and it provides a unified interface for Git, CVS, Mercurial, Subversion, and Perforce. Other features include bookmarks and To-Dos that help keep track of your progress.
PyCharm is available in two different versions: The Community Edition and the Professional Edition. The Community Edition is free and open-source, whereas the Professional Edition is a paid version. You can try the Professional Edition first as part of the 30-day free trial before paying for it. You will have to buy a licence after that period.
Both versions offer features such as an amazing Python editor, graphical debugger and test runner, navigation and refactorings, code inspections, and VCS support. In addition to these, the Professional Edition also features scientific tools, web development features, Python web frameworks, Python profiler, remote development capabilities, and database & SQL support.
Jupyter: Key Features
Jupyter is another incredibly popular Python IDE. As a web application, Jupyter stands out from most other IDEs. It operates on a server-client structure, and you can use it directly from your web browser without the need to install anything. The name 'Jupyter' refers to the three most popular programming languages supported by this platform: Julia, Python, and R.
From the main menu, choose Tools | Open CProfile snapshot.
In the Select PStat file dialog, choose the desired file with the extension pstat.
The profiling results open in the .pstat tab in the editor.
PyCharm and Jupyter are two very popular environments among Python developers and data scientists. Both these environments offer their own set of advantages. But which between the two should a data scientist pick?
Both PyCharm and Jupyter have their advantages in data science. Jupyter is more suitable as a prototyping tool for prototyping models and doing a quick analysis of data. PyCharm is generally suitable for building complex multi-layered applications that can analyze large data sets.
In this article, we will explore this subject in detail. We will start off by looking at the key features of each of these platforms. Next, we will differentiate between them and then finally discuss which of them is the better choice for data science.
PyCharm: Key Features
PyCharm is a Python IDE developed by JetBrains. It is one of the most popular Python IDEs among developers, and there are several reasons behind this.
First and foremost, PyCharm has one of the best code editors among all the Python IDEs. It features all the basic features like code analysis, quick fixes, syntax/error highlighting as well as additional features like code folder, auto-code generation, auto-indentation, etc. Navigating across your codebase is also incredibly easy with PyCharm thanks to features like an easy location for the usage of a symbol.
Additional features include a powerful debugger that comes with a graphical interface as well as integrated unit testing capability that presents the results graphically. A cool version control system is integrated within PyCharm, and it provides a unified interface for Git, CVS, Mercurial, Subversion, and Perforce. Other features include bookmarks and To-Dos that help keep track of your progress.
PyCharm is available in two different versions: The Community Edition and the Professional Edition. The Community Edition is free and open-source, whereas the Professional Edition is a paid version. You can try the Professional Edition first as part of the 30-day free trial before paying for it. You will have to buy a licence after that period.
Both versions offer features such as an amazing Python editor, graphical debugger and test runner, navigation and refactorings, code inspections, and VCS support. In addition to these, the Professional Edition also features scientific tools, web development features, Python web frameworks, Python profiler, remote development capabilities, and database & SQL support.
Jupyter: Key Features
Jupyter is another incredibly popular Python IDE. As a web application, Jupyter stands out from most other IDEs. It operates on a server-client structure, and you can use it directly from your web browser without the need to install anything. The name 'Jupyter' refers to the three most popular programming languages supported by this platform: Julia, Python, and R.
Project Jupyter offers several different applications. For Python, the classic Jupyter Notebook is the more established application. Another Python application, JupyterLab, was launched in 2018 with a special focus on data science.
One of the coolest things about Jupyter is that it is incredibly easy to use for beginners. This is because it allows you to both write your code and then test it in the same interface. But this doesn't mean Jupyter's usability is limited to beginners.
One cool feature that even experts find helpful is the creation of notebooks, with explanations and visualizations. These notebooks can later be downloaded as pdf files, ‘.py' files, or in other formats.
The interface is extremely intuitive. It features the terminal, text editor, file directory, and console all in a single layout. The interface can also be customized using features such as magic commands or notebook extensions.
A Zen mode is available to minimize the interface by removing as many distractions as possible. You can also choose to add a range of other features like autosave, auto-format, debugging, etc.
PyCharm vs. Jupyter: Key Differences
Now that we've looked at the key features of both PyCharm and Jupyter, let us compare these IDEs by analyzing their features side by side:
Which One Should You Use for Data Science?
Both PyCharm and Jupyter have their own set of advantages.
In short, Jupyter is the more suitable option when you have quick data processing and visualization tasks at hand. In other words, Jupyter can be great as a rapid prototyping and visualization tool.
On the other hand, PyCharm is more suited for complex data processing. Think about scenarios where you're dealing with large and dynamic data sets that require long term analysis. You will want to develop a complex application for this, and PyCharm is much better at handling this.
As a professional data scientist, there will be plenty of instances where you'll have to build a complex data analytics tool. There will also be plenty of instances where you'll be required to do a quick analysis and data visualization. Thus both Jupyter and PyCharm will have their use cases. So it will help your career as a data scientist to learn and master both these tools.
If you are looking to work as an entry-level data scientist or you're a student of data science, you can go ahead and start off by learning Jupyter. Jupyter offers interactive outputs, meaning you can write your code and then test it within the same interface. This is a very helpful feature for beginners. The overall interface is also easier to work with, featuring all the tools you will need as a data scientist under the same work environment.
Once you become a more established data scientist, you can start using PyCharm as well. Like we've mentioned previously, as a professional, you will be using both of these environments.
Conclusion
There will be instances in a data scientist's career where both PyCharm and Jypyter will have their advantages over the other. PyCharm is the IDE of choice for a majority of Python developers. As such, it is specifically advantageous for a data scientist looking to build a dynamic data analysis tool or application that can work with a large data set.
Pycharm Community Edition Eula
Jupyter is much more suitable for most of the basic prototyping of models and analysis of small data sets that a data scientist will be doing throughout his/her career. Furthermore, it offers the option to embed the code, text, and visualization graphics into web pages or share them as notebooks.
Pycharm Community Edition Download
- Bhandari. (2020, July 12). 5 powerful Python IDEs for writing analytics and data science code. Analytics Vidhya. https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2020/06/5-python-ide-analytics-data-science-programming/
- Difference between Jupyter and Pycharm. (2020, July 23). GeeksforGeeks. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-jupyter-and-pycharm/
- Project Jupyter. (n.d.). Project Jupyter. https://jupyter.org/try
- PyCharm: The Python IDE for professional developers by JetBrains. (2020, August 25). JetBrains. https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/

